Lithium Iron Phosphate battery protections
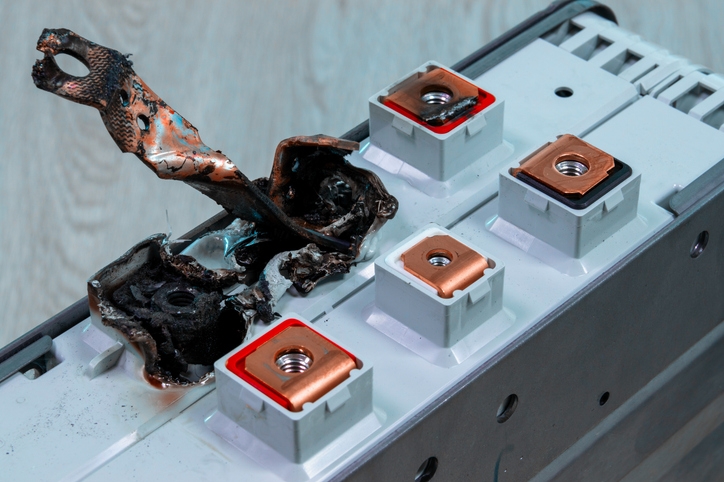
Lithium batteries have one thing in common: their very low internal resistance.
In the event of a short-circuit, this low resistance generates enormous currents. These currents have nothing in common with those encountered in such an event on lead-acid batteries, and require appropriate protective measures. It is therefore important to check your installation before replacing your lead-acid or AGM battery with a lithium battery.
BMS (Battery Management System)
BMS (Battery Management System) is essential to keep each cell of battery pack within the safety operation. It’s a crucial equipment with several functions.
Monitoring
The BMS will continuously monitor the status (voltage, temperature, state of charge) of each module.
This monitoring includes voltage parameters, incoming and outgoing currents, temperatures and balancing (application of identical voltage to the various modules). Thermal runaway, which can result in the battery catching fire or exploding can be brought on by overcharging, over-discharging, high current, or operating outside of the permitted temperature range.
Protection
One of the primary responsibilities of a Battery Management System (BMS) is to safeguard the battery and the system as a whole against conditions that could potentially cause harm or present safety hazards. The BMS carries out protective actions to counteract scenarios such as overcharging, deep discharging, overcurrent, short-circuits, and overheating. For example, if the voltage across a cell surpasses a specific threshold, indicating overcharging, the BMS may disconnect the charging circuit or divert the current to prevent further charging of that particular cell.

Balancing
In a typical battery pack, multiple cells are connected in series or parallel to achieve the desired voltage and capacity. However, due to manufacturing variations and operational conditions, these cells may exhibit slight differences in their capacity and voltage characteristics. Equalization is a crucial task carried out by the BMS to guarantee a uniform State of Charge (SOC) among all cells within a battery pack.
Communication
The most advanced BMS provide a communication port for better complete integration of battery in the complete system. CANBUS, Bluetooth, RS485, UART can read all battery data in real time.
Alternator overheating
Engine diesel generator generally have a basic charging characteristics. Connected to an empty lithium battery, its low internal resistance means that it will demand maximum current from the alternator - a current that most automotive alternators are incapable of delivering over a long period without damage.
This can cause the alternator to overheat and burn-out. Alternators are internally cooled by a fan on its rotor.
To avoid these two problems, we recommend installing a specific alternator with an external regulator and protection via an external temperature sensor, or using the starter battery to divert alternator current to it when the BMS cuts out. Another option is to install a DC/DC charger. Most of Dolphin Booster DC/DC provides a specific charging profile for lithium battery.
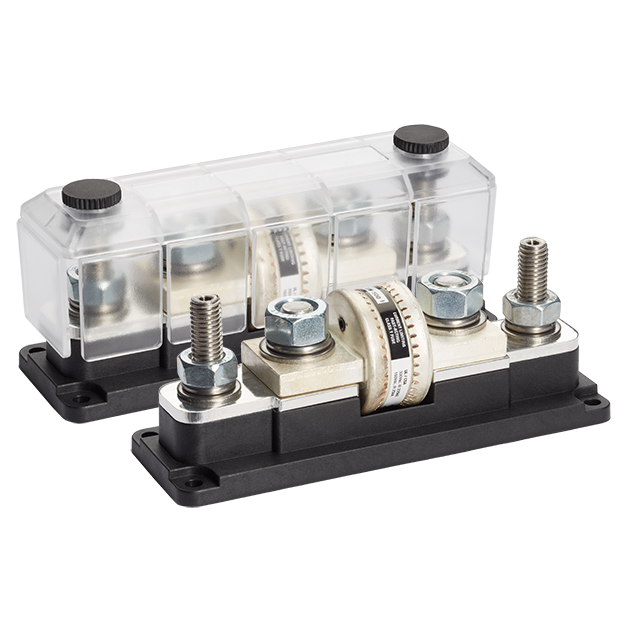
DC Fuses
On a 40 kWh 48 V drive battery, short-circuit currents can reach extreme values, around 20 kA (20,000 A). The choice of fuse rating and type is crucial. Only properly sized fuses can maintain their disconnecting capacity at these very high currents. Class T fuse is perfect to protect equipment in the event of a high overcurrent.
In the event of a short-circuit in the battery, and without properly calibrated protection, all DC (direct current) equipment connected to the battery could be destroyed or damaged by these currents. Fuses that protect individual circuits are designed to protect their cables, and are in no way designed to isolate them from the battery in the event of a short-circuit.
Class T fuses are capable of interrupting a short-circuit current of the order of 20,000 A extremely rapidly, in less than 10 ms. They are distinguished by their rating, the normal current they are designed to withstand.
In the example of our 48 VDC battery, a class T (400 A rating) 48 VDC fuse is capable of interrupting a short-circuit current of 20 kA .
Water protection class for Lithium propulsion batteries
Most of lithium battery manufacturers recommend installation location where direct application with water is avoided. It’s most of time the case in RV’s or special vehicles. For marine application situation could be different.
Water protection should be carefully checked. Without protection, a short-circuit is possible and the electronic protection device, the BMS, is guaranteed to fail...
Only components suitably protected against water ingress to IP 66 or IP 67 should be installed on board boats or under the chassis of recreational vehicles. It is highly recommended to place all lithium ion batteries in a dry lock box to prevent any water damage
Storage
While lithium batteries are more stable than lead-acid units to the point that they rarely emit gasses and fumes, ventilation is still crucial on a vessel. If a lithium battery leaks gas or fumes, it could easily cause an intense and potentially disastrous fire.
As with all batteries, overheating is a significant cause for concern. While lithium batteries are more heat-resistant than lead-acid units, they can still overheat if left in hot and strenuous conditions.
The cold is another potential danger to lithium batteries. Based on geographical location freezing temperature could be also a problem. Do not leave the battery in the cold. Performance of battery will be dramatically reduced in case of negative temperature. This is a reason why many lithium battery are fitted with self-heating device.
Marine and RV specialist Dolphin® Charger range of AC and DC battery charger o full range of products design to comply lithium battery charging specifications. From 10 to 100 amps, dedicated for boating or recreational vehicle market, Dolphin's range of chargers meets every need, without compromising on quality and reliability.


